Featured Content
Learn How Startups Can Harness Power BI and User-Centred Design for Impactful Dashboards
Discover how Startups Power BI User-Centred Design transforms raw data into actionable insights, improving decision-making and business success.
 I believe every startup needs a dashboard that not only tracks numbers but tells a story.
I believe every startup needs a dashboard that not only tracks numbers but tells a story.
The difference between a startup’s success and failure often hinges on how effectively they implement Startup Power BI User-Centred Design to transform raw data into actionable insights. Many startups gather large amounts of data, but the real challenge is presenting it clearly to support informed decision-making. This is where the synergy between Power BI and user-centered design becomes invaluable.
According to Forrester Research (2023), organizations that effectively employ data visualization tools experience a 32% boost in decision-making speed and a 28% increase in data accuracy. Additionally, McKinsey’s most recent study (2023) found that data-driven businesses are 23% more likely to attract consumers and 19% more likely to be profitable.
However, merely adopting a business intelligence tool is insufficient; the key is in creating dashboards that meet users’ demands and provide relevant insights.
The Foundation: Understanding User-Centered Dashboard Design
Comprehensive User Research
Startups aiming to master Startup Power BI User-Centered Design must begin with comprehensive user research.
Stakeholder Interviews
- Understand specific goals and pain points
- Identify key metrics and KPIs
- Define success criteria
- Document reporting frequencies
User Personas Development
- Executive Level: Needs high-level strategic insights
- Operations Team: Requires detailed daily metrics
- Sales Team: Focuses on pipeline and conversion data
- Marketing Team: Tracks campaign performance
- Product Team: Monitors user engagement metrics
Organizing Data Structure
Organize your data structure based on the following:
- Business objectives
- User workflows
- Data relationships
- Access requirements
- Update frequencies
Design Principles for Maximum Impact
Visual Hierarchy
- Place crucial information in prime viewing areas
- Use size and color to indicate importance
- Implement consistent spacing
- Create clear visual pathways
Color Psychology
- Use brand colors appropriately
- Use colors for meaning (red for alerts, green for success)
- Ensure accessibility for color-blind users
- Maintain consistent color coding
Building Effective Dashboards in Power BI
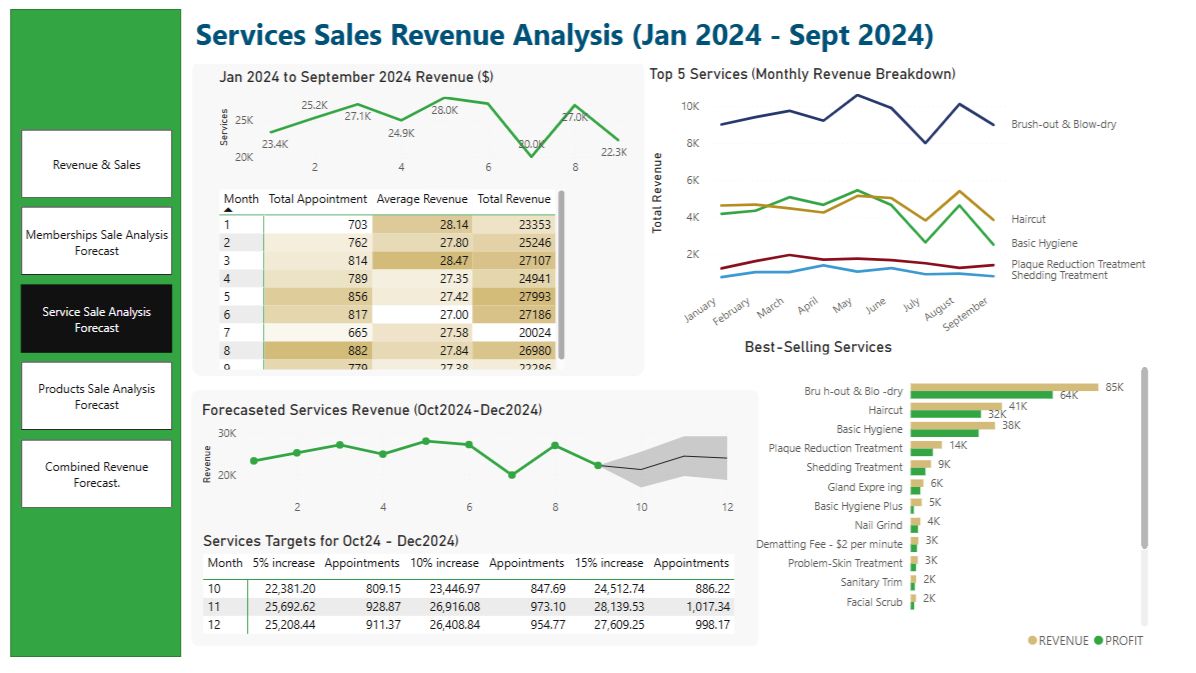 Power BI helps businesses streamline data into clear, actionable insights—making decision-making faster, easier, and more confident.
Power BI helps businesses streamline data into clear, actionable insights—making decision-making faster, easier, and more confident.
Strategic Planning Phase
Before opening Power BI, develop:
- Clear dashboard objectives
- Key metric requirements
- Data source mapping
- Update frequency plans
- Security requirements
Layout Best Practices
Page Structure
- Overview page for high-level metrics
- Detailed pages for specific areas
- Drill-through pages for deep understanding
- Filter panels for customization
Visual Organization
- Group related metrics together
- Implement consistent spacing
- Use grid alignment
- Maintain visual balance
Visual Selection Guidelines
Choose appropriate visualizations based on data type:
Comparison Data
- Bar charts for static comparisons
- Column charts for time-based comparisons
- Bullet charts for targets vs. actuals
Trend Analysis
- Line charts for continuous data
- Area charts for cumulative trends
- Sparklines for quick trends
Part-to-Whole Relationships
- Use pie charts sparingly
- Treemaps for hierarchical data
- Stacked bars for component analysis
Interactive Design Elements
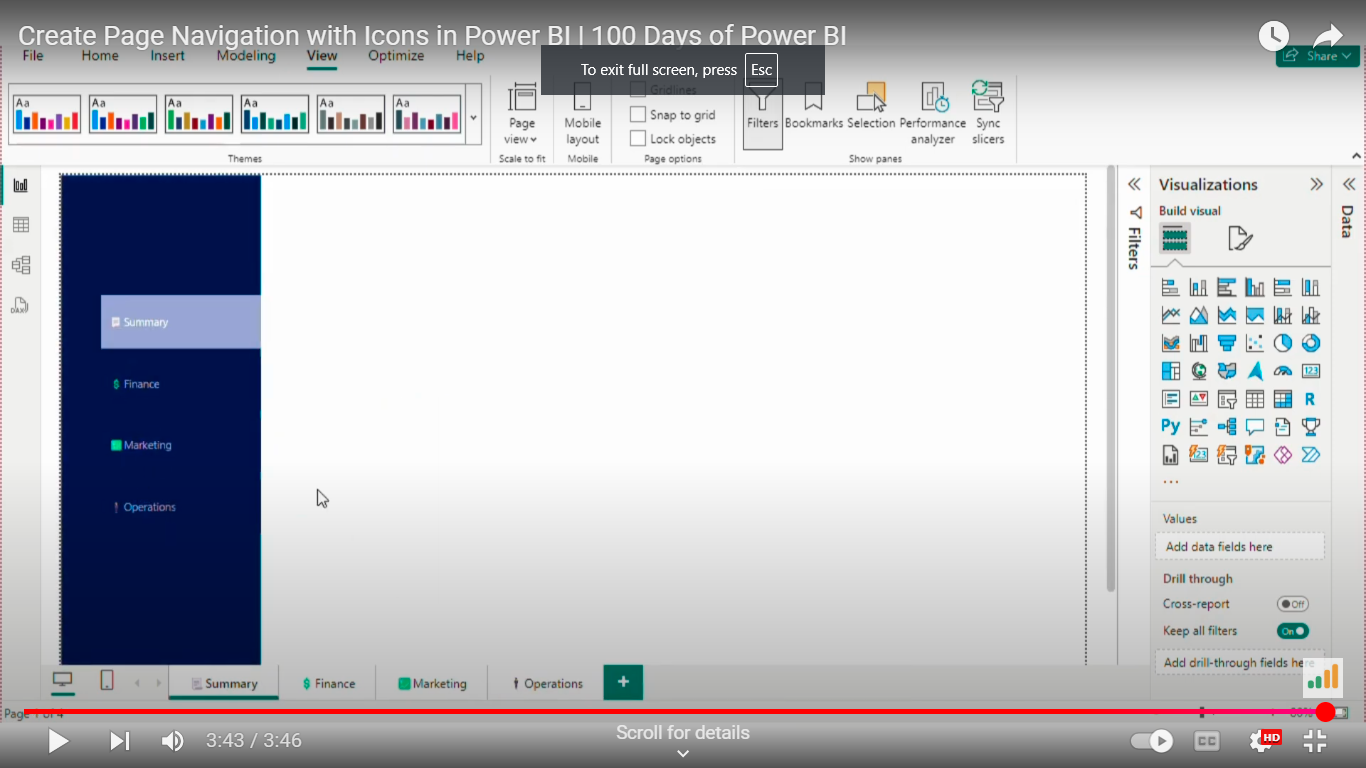 Create Page Navigation with Icons in Power BI.
Create Page Navigation with Icons in Power BI.
Navigation Framework
Clear Menu Structure
- Logical page hierarchy
- Consistent navigation patterns
- Breadcrumb trails
- Quick access to key pages
Filter Design
- Global filters for cross-page analysis
- Page-level filters for specific views
- Cascading filters for detailed analysis
- Clear filter state indicators
User Interaction Features
Drill-Down Capabilities
- Hierarchical navigation
- Context-preserving transitions
- Back-navigation options
- Clear drill-path indicators
Custom Tooltips
- Relevant additional information
- Contextual insights
- Related metrics
- Action triggers
Case Study: E-commerce Dashboard Transformation
An emerging e-commerce firm with over 50 workers and $5 million in yearly revenue faced challenges that could be addressed through Startup Power BI User-Centered Design, including data fragmentation and delayed decision-making.
Initial Challenges
- Data scattered across seven different platforms
- 4-5 hours spent weekly on manual reporting
- A 20% error rate in manual data compilation
- Low user adoption of existing dashboards (15%)
Solution Implementation
1. Discovery Phase
- Conducted 5+ user interviews
- Created four distinct user personas
- Mapped 15 critical business processes
- Identified 30 essential metrics
2. Dashboard Development
Executive Dashboard
- Daily sales overview with hourly updates
- Inventory health metrics
- Customer satisfaction scores
- Financial performance indicators
Operations Dashboard
- Real-time inventory levels
- Order fulfillment metrics
- Supply chain visibility
- Warehouse performance
Customer Insights Dashboard
- Customer behavior patterns
- Purchase history analysis
- Customer satisfaction trends
- Return rate monitoring
Measurable Results
- 40% reduction in reporting time
- 25% improvement in inventory management
- 30% increase in dashboard user adoption
- 95% user satisfaction rate
- 50% faster decision-making process
Best Practices for Sustainable Success
Performance Optimization
Data Refresh Strategy
- Implement incremental refreshes
- Schedule updates during off-peak hours
- Monitor refresh success rates
- Optimize semantic models
Regular Maintenance
- Weekly performance checks
- Monthly user feedback reviews
- Quarterly feature updates
- Annual comprehensive review
User Adoption Strategy
Training Program
- Initial onboarding sessions
- Regular workshop sessions
- Video tutorials
- Quick reference guides
Support Structure
- Dedicated support channel
- FAQ documentation
- User feedback system
- Regular check-ins
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Design Mistakes
- Overcrowding pages with too many visuals
- Using inappropriate chart types
- Inconsistent formatting
- Poor mobile optimization
Technical Issues
- Slow refresh rates
- Complex semantic models
- Insufficient testing
- Poor documentation
User Experience Problems
- Confusing navigation
- Insufficient user training
- Lack of context
- Poor feedback implementation
Future-Proofing Your Dashboards
Scalability Considerations
- Plan for data growth
- Consider additional user types
- Allow for metric evolution
- Build flexible layouts
Technology Integration
- API connectivity options
- Cross-platform compatibility
- Mobile responsiveness
- Security updates
Conclusion
Creating effective dashboards is an iterative process that requires a thorough understanding of technical capabilities and user requirements.
Success comes from:
- Thorough user research and comprehension
- Careful planning and design
- Regular feedback and iteration
- Focus on simplicity and clarity
- Commitment to Continuous Improvement
Remember, even the most complex dashboard is only as effective as its capacity to drive actions and decisions. By adhering to these principles and rules, startups may design Power BI dashboards that appear professional and become crucial tools for business success.
The idea is to begin with user needs, build with purpose, and iterate based on feedback and evolving business requirements. By adopting this technique, your Power BI dashboards will be a key driver of your startup’s growth and success.








Comments
Share your take or ask a question below.